this post was submitted on 07 Apr 2024
42 points (100.0% liked)
Earth
12837 readers
21 users here now
The world’s #1 planet!
A community for the discussion of the environment, climate change, ecology, sustainability, nature, and pictures of cute wild animals.
Socialism is the only path out of the global ecological crisis.
founded 3 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
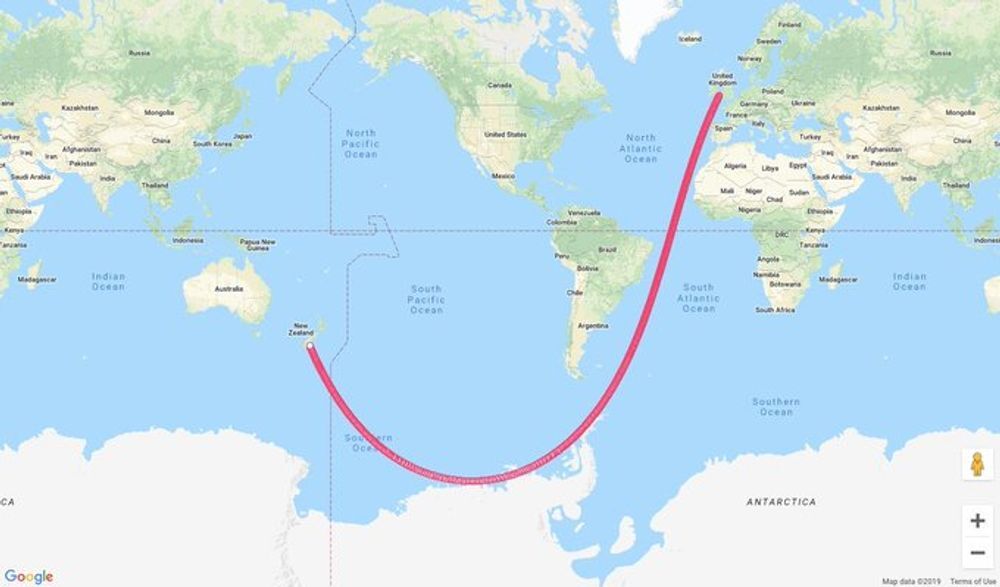

TL;DR being able to talk about curvature in a mathematical way outside of a euclidean space is a chore because it needs differentiation and its best to let your intuition guide you when talking about these concepts because "walking straight on a sphere" is imo clear enough.
A differentiable manifold holds the key. Start with a topological space. So the points in ℝ^3^ you described along with the by the ℝ^3^ induced topology is indeed the goto. Note that the radius of the sphere no longer matters as any sphere can be projected onto any other homeomorphically.
Then define homeomorphic maps from open subsets of the ℝ^2^ onto the sphere until its covered. At least two such maps are necessary. The key is now that the maps necessarily have to overlap on the sphere and we thus get maps from an open subset in the ℝ^2^ to another open subset of the ℝ^2^ by using one map go to the sphere and the inverse of another overlapping map to go back to the ℝ^2^. By requiring that these functions be diffeomorphic we transport the structure required for calculus to the sphere and we can talk about the curvature of a path. Then we can observe the existance of straight line by describing a path with no curvature on the sphere.
Because of the requirement of diffeomorphism the structure is unique, i. e. any other such structure can be diffeomorphically mapped to eachother and we can switch out maps as we please without changing any properties of the objects constructed.
By this I meant that if you take any projection of the sphere onto a flat surface, use it to project a line without curvature on the sphere to the flat surface the line thusly obtained will be curved w.r.t. the structure of the flat surface.
edit: this is obviously incorrect as any world map will show apologies. I should have said that there is a projection for any straight line on the sphere which will map it to a curved one in the 2d space.