(Images can be enlarged if needed)
Cardiac arrest, also known as Sudden Cardiac Arrest, is when the heart stops beating suddenly. The lack of blood flow to the brain and other organs can cause a person to lose consciousness, become disabled or die if not treated immediately.
The terms ‘heart attack’ and ‘cardiac arrest’ are often used interchangeably, but these are two different heart conditions.
A heart attack occurs when there is a blockage in the arteries that stops blood flow in the heart. Due to the lack of blood and oxygen flowing in the heart, the heart muscle tissue will become damaged. Heart attacks can increase the risk for cardiac arrest because heart attacks can alter electrical signals in the heart.
CPR – or Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation – is an emergency lifesaving procedure performed when the heart stops beating. Immediate CPR can double or triple chances of survival after cardiac arrest.
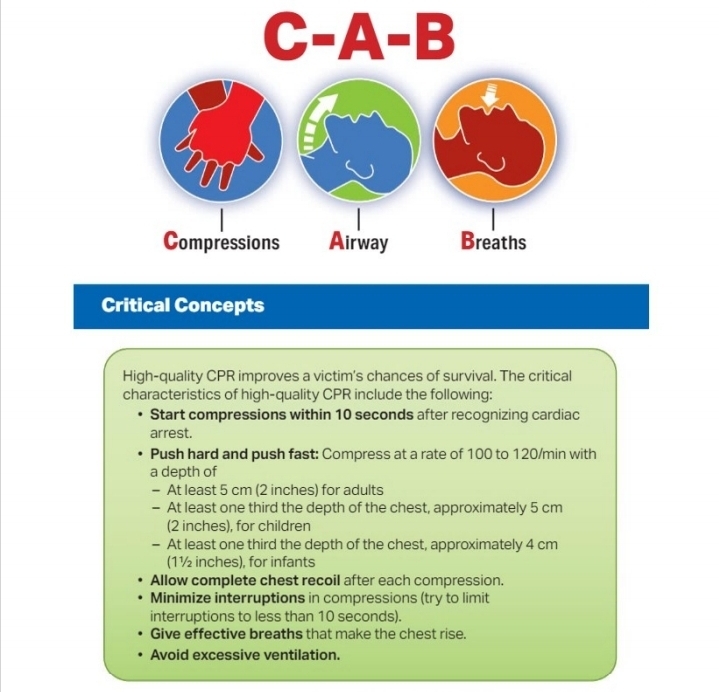
If someone experiences cardiac arrest, they need immediate treatment to increase the flow of oxygen-rich blood to their organs. CPR is the compression over the chest to manually pump a patients heart. Rescue breaths are preformed to provide oxygen to the body.
During CPR, proper hand placement on the lower half of the sternum is crucial. Placing hands over the sternum ensures effective chest compressions directly above the heart, optimizing blood circulation throughout the body.
According to the American Heart Association (AHA), the overall survival rate for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is around 10%. However, survival rates can be improved if bystander CPR is started immediately. Studies have shown that bystander CPR increases the chances of survival for someone experiencing cardiac arrest. In fact, the AHA reports that survival rates increases to 40% or higher when bystander CPR is performed promptly. The surival rate is between 24% and 40% for those that happen in the hospital, according to the report published online in the Emergency Medicine Journal.
CPR is preformed between 100 - 120 beats per minute. Famously Staying Alive by the Bee Gees is the same beat. A large list of songs with the correct BPM can be found here
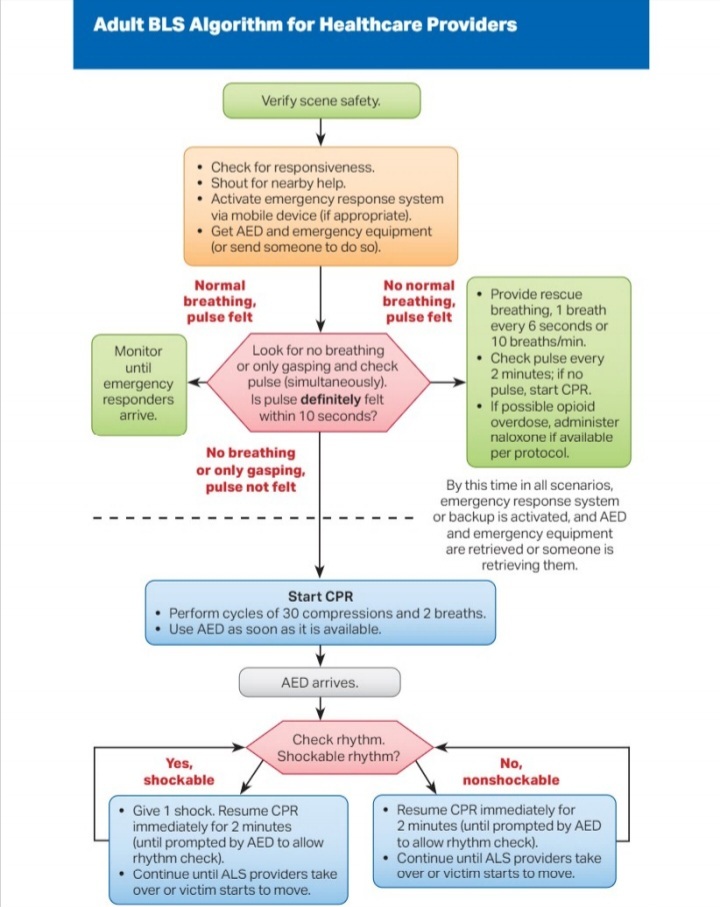
 The American Red Cross gives the following list of steps to asses if CPR is needed and how to preform:
The American Red Cross gives the following list of steps to asses if CPR is needed and how to preform:
1 CHECK the scene for safety, form an initial impression and use personal protective equipment (PPE)
2 If the person appears unresponsive, CHECK for responsiveness, breathing, life-threatening bleeding or other life-threatening conditions using shout-tap-shout
3 If the person does not respond and is not breathing or only gasping, CALL 9-1-1 and get equipment, or tell someone to do so
4 Kneel beside the person. Place the person on their back on a firm, flat surface
5 The American Red Cross CPR guidelines recommend 100 to 120 chest compressions per minute, 30 at a time. Remember these five points:
Hand position: Two hands centered on the chest
Body position: Shoulders directly over hands; elbows locked
Compression depth: At least 2 inches
Rate of compressions: 100 to 120 per minute
Allow chest to return to normal position after each compression
6
Give 2 breaths
Open the airway to a past-neutral position using the head-tilt/chin-lift technique Pinch the nose shut, take a normal breath, and make complete seal over the person’s mouth with your mouth. Ensure each breath lasts about 1 second and makes the chest rise; allow air to exit before giving the next breath Note: If the 1st breath does not cause the chest to rise, retilt the head and ensure a proper seal before giving the 2nd breath If the 2nd breath does not make the chest rise, an object may be blocking the airway
7 Continue giving sets of 30 chest compressions and 2 breaths. Use an AED as soon as one is available! Minimize interruptions to chest compressions to less than 10 seconds.
Sources:
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/cardiac-arrest
https://cpr.heart.org/en/resources/cpr-facts-and-stats
https://www.mycprcertificationonline.com/blog/cpr-success-rate
Instructional images from the AHS Basic Life Support Manual (2020)
Join our public Matrix server! https://matrix.to/#/#tracha:chapo.chat
As a reminder, be sure to properly give content warnings and put sensitive subjects behind proper spoiler tags. It's for the mental health of not just your comrades, but yourself as well.
Here is a screenshot of where to find the spoiler button.

trauma/abuse
I have been talking with my two closest friends about some of my childhood. They both think my parents were abusive.I don't know how to process this. I have been in fight or flight for the last like, day. I didn't eat yesterday. Got like three hours of sleep at 7am. I have cried so much. After finally telling someone some of what I remember its just... so sad. They loved me... but still did things I have had trouble getting over since. I have wondered for a while. I knew it was wrong, I knew it made me feel awful, and scared, and many other things... but it felt normal. I blame(d) myself.
I feel sad. Numb. Broken. I feel/have felt for a long time that what I dealt with was not enough to be legitimate. I'm still denying it a little bit. I guess always feeling on edge/a bit scared around dad makes sense with this framework though... spoiler self harm I am fighting the urges. My brain is convinced this would be easier to deal with if I did it. I am keeping myself from doing it only because I feel like other people would say its bad. ::: Thank you for reading. I am feeling a lot and I don't know how to deal with it. Advice is welcome, I'm not ready to talk about details though so please don't ask.
abuse
When I first got the inkling that maybe my parents were being abusive to me, I denied it. Hard. For years, and actually I'm still struggling with that denial. I also feel like what I went through wasn't enough to be legitimate abuse, because my parents cared for me! They could have been a lot worse! They wanted me to be happy!The thing is — society likes to view abuse as something exceptional, to assign it to bad individuals, when the reality is that abuse is a method of enforcing a power system. It's normal, and incredibly common, because it's how our society runs. At the base level, capitalism is basically a structure of continual abuse; and the superstructure reflects that. Parental abuse is the method by which the structures of patriarchy and childism are enforced — viewing children as property, not as full humans. Back during feudalism, children were essentially a family business investment; under capitalism, we are purposefully sequestered into nuclear families.
My parents can exert their power over me because under their roof and under their dollar, I functionally have no power of my own. Especially as living conditions continue to decline and many millenials/gen-z are unable to find stable housing and jobs on their own, many are forced into these kinds of situations where abuse is basically a natural outgrowth of the systems in place. Additionally, the way my parents treat me is a way of enforcing their standards of normativity. I'm too weird, too mentally ill for them. Many disabled/neurodivergent people live in abusive situations because of a combination of these two factors.
I don't know if any of this is helpful. But I do just want to say — it's not your fault, and your experiences are real and valid. It's not right that you should feel on edge around your dad. And self-blame is a huge part of processing abuse, but I believe it gets better with time. I'm sorry, I wish life wasn't so awful.
Sorry for taking so long to get back to you. This is all very helpful, thank you for telling me. I will keep trying.